Purpose for coding
For the management of highway competent authority
The transmission of the highway information is the focus of the highway management work. The transmission or report of the information shall be brief and clear; for example, if you use a long road name to describe the location on the road where a disaster or traffic accident happened, it is not only difficult to understand, but also difficult to express clearly in a short sentence. Using highway number and the mileage location marking is simple, convenient and with no misunderstanding. Therefore, the purpose of highway coding is to make the management easier for highway competent authority.
Easy utilization for road users
Highway construction is to provide traffic services, and all policies and regulations shall be based on the convenience to road users. The higher the highway level, such as national freeway and provincial highway, is for the purpose to reach the destination in the shortest time, and it is with higher mobility and lower accessibility in terms of traffic function. On the contrary, district highways and country roads provide access to different local regions, with higher accessibility but lower mobility in terms of traffic function. That is, road users choose to drive on the highway because they want to reach their destination quickly, comfortably, and safely. Thus, they will select driving routes between the departure point and arrival point before their journey. If there is no numbers provided for highways, it will not only take longer to make the choice, but also provide no information on the level of highway. As a result, it tends to cause misjudgment and fails the purpose of arrival to the destination in the shortest time. In addition, even though road users are able to select a proper route between the starting and ending places, it often feels like driving into a maze and finds no way out when the route passes district, county, town, or city and enter the city street. If a highway number is provided, it will easy to navigate through city center with the highway number and mark of name of place heading for.
Development history of coding
The management of highway in our country is at least 50 years late than the management of railway. Before the victory of the war of resistance against Japanese aggression (1945), we usually use the code letter between the two places or two areas as the name of the road; for example, Kangching Highway between Kangding to Chinghai. There was no highway management system established and no mention of highway number. In July 1947, Executive Yuan announced national freeway network plan and that was the start of coding like “Chi 4”, “Ching 5”, “Wei 6”, and 22 road numbers for latitude and longitude connecting roads; it was the origin of the highway coding in our country. The highway coding mentioned above was only for important national freeway network, but there was no idea on the coding of provincial highway and county highway; there was no consideration of coding for country road. For the national freeway that has already been coded, it had never been formally implemented due to Republic of China retreat to Taiwan. The roads in Taiwan had no coding system before 1961, and they were usually named by the habit of road management at that moment. For example, the North-South Highway in Japanese occupation period was called Western Line after the restoration of Taiwan and it was coded as Provincial Highway No. 1 afterwards. The Eastern Line in the past was coded Provincial Highway No. 9 afterwards. The two highways can be seen as the representative of highway naming in Taiwan. Until July 1961, our Directorate General held highway survey and the road system was divided into provincial highway, county highway, and country road (no national freeway at that moment) based on the highway distribution at that moment according to the Highway Act implemented in July, 1960. However, in order to reflect the actual situation of the county highway and country roads entrusted to province for management when implementing the coding, the county highway and country roads were combined together and divided into “major county highway and country roads” and “minor county highway and country roads”. All the major county highway and country roads followed the same coding for county highway while minor county highway and country roads followed the same coding as country roads. In 1962, coding for the roads all over Taiwan was completed and it was the beginning of coding for highway in Taiwan Province.
 On December 12th, 1963, Taiwan Province Government formally published “Taiwan Province Highways and Highway Bridges Coding Methods” and requested each local government to comply with the rules for implementation. On February 27th, 1965, Ministry of Transportation and Communications published “Rules for Highway Construction and Maintenance”. In Article 9, it specified “Highway competent authority should code highway based on the left-listing principle according to the road system published”. In the principle, the difference from the regulation published by Taiwan Province Government was north-south route shall be coded from the east to the west while east-west route shall use the east as the starting point. When it was revised to “Management Rules for Highway Construction and Maintenance” in July 1973, the basic principle was not changed other than the article order was revised to 11 articles. The “Management Rules for Highway Construction and Maintenance” was formulated by Ministry of Transportation and Communications according to the whole geography of China. However, in order to consider the special environment in island, like Taiwan and Hainan, a proviso of “the highway coding in the area of island shall be flexible based on the actual situation” was added. Because we had Taiwan Province highway number before the rules for coding and the legal regulations from central government came even later, the highway coding principle in Taiwan Province belong to the flexible scope permitted by the proviso. Therefore, the north-south routes in Taiwan Province were coded from the west to the east, and the east-west routes was coded from the west.
On December 12th, 1963, Taiwan Province Government formally published “Taiwan Province Highways and Highway Bridges Coding Methods” and requested each local government to comply with the rules for implementation. On February 27th, 1965, Ministry of Transportation and Communications published “Rules for Highway Construction and Maintenance”. In Article 9, it specified “Highway competent authority should code highway based on the left-listing principle according to the road system published”. In the principle, the difference from the regulation published by Taiwan Province Government was north-south route shall be coded from the east to the west while east-west route shall use the east as the starting point. When it was revised to “Management Rules for Highway Construction and Maintenance” in July 1973, the basic principle was not changed other than the article order was revised to 11 articles. The “Management Rules for Highway Construction and Maintenance” was formulated by Ministry of Transportation and Communications according to the whole geography of China. However, in order to consider the special environment in island, like Taiwan and Hainan, a proviso of “the highway coding in the area of island shall be flexible based on the actual situation” was added. Because we had Taiwan Province highway number before the rules for coding and the legal regulations from central government came even later, the highway coding principle in Taiwan Province belong to the flexible scope permitted by the proviso. Therefore, the north-south routes in Taiwan Province were coded from the west to the east, and the east-west routes was coded from the west.
 In July 1973, our Directorate General held the first highway facility engineering facility general inspection, consolidating and organized some highway routes, as well as added and modified some coding. In 1977, highway numbers were comprehensively corrected in a wide range to cooperate with the planning of new highway network in Taiwan. Executive Yuan approved on August 24th, 1977 and announced by Ministry of Transportation and Communications published the highway network and its coding on July 1st, 1978. Among it, the biggest change was to cancel the classification of major county highway and country roads and minor county highway and country roads, fully adhering to county highways and country roads for coding. Meanwhile, cancel the individual coding for routes what can be integrated in the future and consolidate it into one number. Some major country road also turned into county highway in the announcement.
In July 1973, our Directorate General held the first highway facility engineering facility general inspection, consolidating and organized some highway routes, as well as added and modified some coding. In 1977, highway numbers were comprehensively corrected in a wide range to cooperate with the planning of new highway network in Taiwan. Executive Yuan approved on August 24th, 1977 and announced by Ministry of Transportation and Communications published the highway network and its coding on July 1st, 1978. Among it, the biggest change was to cancel the classification of major county highway and country roads and minor county highway and country roads, fully adhering to county highways and country roads for coding. Meanwhile, cancel the individual coding for routes what can be integrated in the future and consolidate it into one number. Some major country road also turned into county highway in the announcement.
Highway coding follows the provisions of Article 15 and Article 16 of “Rules for Highway Construction and Maintenance”. Its principle is as below:
- The order of highway coding:
- Routes with a direction of west to east shall be coded with even number from north to south.
- Routes with a direction of north to south shall be coded with odd number from west to east.
- The route with feeder number shall be connected to the main route on one end, and it shall be coded by the original route number plus an English letter or a number.
- The starting point of highway route direction and mileage:
- From north to south
- From northeast to southeast
- From west to east
- From northwest to southeast
- Provincial highway coding: From No.1 to No. 99.
- City road and county road coding: From No. 101.
- District road and country road coding: Start from No. 1 if it is based on municipality or county as well as adding the short form of the municipality or county; for example, the district road located in New Taipei City will have the short form of “Bei” while the country road in Hsinchu County will have a short form of “Chu”.
- Marking for coding :
- National route coding marking
 . It refers to National Freeway No. 1.
. It refers to National Freeway No. 1.
- Provincial highway coding marking
 . It refers to Provincial Highway No. 3. The starting and ending locations of each rout, the name of place passing by, and mileage are shown on the table of provincial highway routes.
. It refers to Provincial Highway No. 3. The starting and ending locations of each rout, the name of place passing by, and mileage are shown on the table of provincial highway routes.
- Provincial route coding marking for expressway
 . It refers to Provincial Highway No. 78.
. It refers to Provincial Highway No. 78.
- City road and country road route coding marking
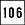 . It refers to City Road No. 106. The starting and ending locations of each rout, the name of place passing by, and mileage are shown on the table of city road and county road routes.
. It refers to City Road No. 106. The starting and ending locations of each rout, the name of place passing by, and mileage are shown on the table of city road and county road routes.
- District road and country road route coding marking
 . It refers to Country Road Chu No. 22.
. It refers to Country Road Chu No. 22.